Shikimate Kinase
Shikimate kinase (SK, EC 2.7.1.71), the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of shikimic acid into shikimate 3-phosphate. SK is essential in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Helicobacter pylori, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc. and it is a recognized attractive target for the development of new drugs against several important bacterial diseases.
Based on structural and computational studies of the Michaelis complex (Scheme 1) and the catalytic turnover of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis shikimate kinase enzyme (Scheme 2) we have designed several substrate analogs (Figure 1).
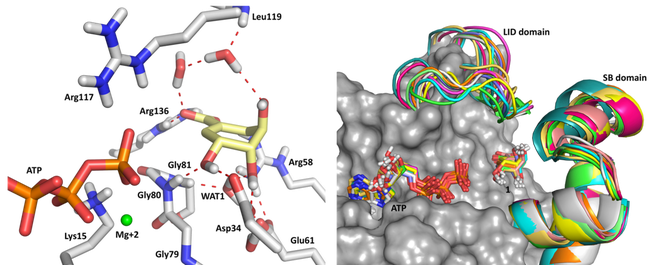
Scheme 1. Relevant binding interactions of shikimic acid in the active site of Mt-SK and comparison of the several
snapshots of the key enzyme domains and the position of both substrates during 10 ns of dynamic simulation.

Scheme 2. Snapshots of shikimate-3-phosphate (yellow) release from the active site of Mt-SK obtained by Molecular
Dynamics simulations studies.
Figure 1. Crystal Structure of ternary complex Mt-SK/ADP/rigid shikimic acid analog (PDB code
4BQS).